how come snakes are meat eaters?
Questions, when asked by wondering minds do not necessarily need a context. Perhaps context, like a place, may give a sense of reality. That context started on a late evening when the lingering reluctant light gave way to darkness. Narayan wanted to go along for the walk. As we went past these woods to our left on the sidewalk, he asked
"Are snakes meat eaters?"
"Yes. I think they are"
"How come?"
"What else should they eat?"
"Well they could eat grass...."
"Ummmm..." was all I could say at the moment.
satya - Friday, May 02, 2008 11:04:39 PM
where do snakes fall on the evolutionary time line?
Search for: where do snakes fall on the evolutionary time line?
satya - Friday, May 02, 2008 11:10:27 PM
classification of snakes
kingdom: animals phylum: chordata class: reptila order: squmata
satya - Friday, May 02, 2008 11:24:34 PM
chordata is vertebrates
chordata is vertebrates
satya - Friday, May 02, 2008 11:25:06 PM
reptiles are a class of vertabrates
reptiles are a class of vertabrates
satya - Friday, May 02, 2008 11:25:51 PM
they are generally cold blodded, scaly skins, and lays eggs
they are generally cold blodded, scaly skins, and lays eggs
satya - Friday, May 02, 2008 11:26:09 PM
in that sense crocodoiles and snakes are cousins
in that sense crocodoiles and snakes are cousins
satya - Friday, May 02, 2008 11:26:37 PM
how old are snakes in the evolutionary line?
satya - Friday, May 02, 2008 11:38:31 PM
evolution of snakes: around the time of dinosaurs
satya - Saturday, May 03, 2008 9:08:09 AM
cotylosaur, anapsid, synapsid, diapsid
satya - Saturday, May 03, 2008 9:08:40 AM
dinosaurs, if they were to be lizards, were they cold bloded?
dinosaurs, if they were to be lizards, were they cold bloded?
satya - Saturday, May 03, 2008 9:10:35 AM
most likely evolution path
Based on these fossil finds, as well as on anatomical study of modern reptiles, scientists have concluded that the snakes probably evolved from a family of lizards during the time of the dinosaurs. Snakes and lizards share a number of distinct features in the structure of their skull; both, for instance, possess a moveable quadrate bone at the back of the jaw, and both are missing the quadratojugal bone at the rear of the skull.
satya - Saturday, May 03, 2008 9:11:59 AM
herpetology is the study of snakes
herpetology is the study of snakes
satya - Saturday, May 03, 2008 9:13:59 AM
How did snakes loose their ears?
Based on these similarities, some herpetologists have theorized that an ancient group of monitor-like lizards began to follow a burrowing way of life, tunneling through loose dirt and sand in search of earthworms and other prey, just as some lizards do today. Over a period of millions of years, these burrowing lizards lost their limbs and their external ears--to help them burrow more easily--and also replaced their eyelids with a clear brille or spectacle to protect their eyes while digging. At about the time that the dinosaurs reached their apex, one group of these burrowing lizards then gave up its subterranean lifestyle and emerged to the surface, where they developed a new legless mode of locomotion and rapidly diversified to invade a large number of ecological niches. Today we classify the various descendants of these legless lizards as snakes.
The "burrowing ancestors" theory has, however, come under some attack recently. Several herpetologists have pointed out that the Dinilysia skull does not show many features adapted to a burrowing existence. Some biologists have theorized that the snake's unique features are the result of a largely aquatic or semi-aquatic lifestyle, as illustrated by the Earless Monitor. In this interpretation, the lack of ears, the covered eyes and the long limbless bodies allowed the first snakes to move efficiently through water or wet marshy areas in search of prey. It was only later that snakes moved from an aquatic environment to invade the dry land. During the time that snakes developed, the Varanid family did contain a number of semi-aquatic and marine species, including the giant Mososaurs.
satya - Saturday, May 03, 2008 9:21:17 AM
are dinosaurs warmbloded?
satya - Saturday, May 03, 2008 9:31:30 AM
are all lizards meat eaters?
well lizards are and crocs are but not turtles. turtles seem to eat vegitation.
satya - Saturday, May 03, 2008 9:38:53 AM
Looks like they are warmbloded according to isotope study
satya - Tuesday, May 06, 2008 11:18:30 AM
interesting article on predators
satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 10:22:38 AM
reptiles
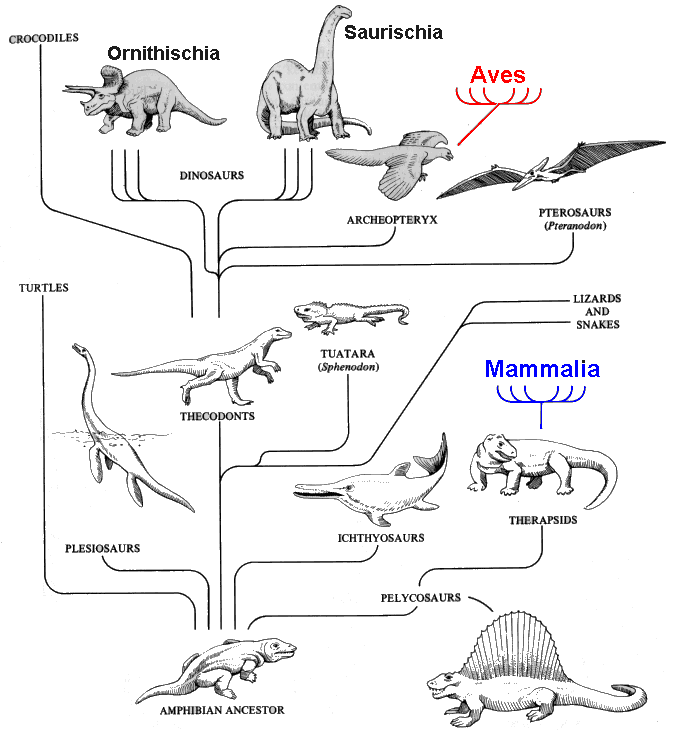
satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 10:24:23 AM
reference to snakes

satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 10:25:37 AM
Taken from ritchisong, comparative vertebrate anatomy
satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 10:27:37 AM
what are the eating habits of cotylosaurs?
what are the eating habits of cotylosaurs?
satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 10:28:04 AM
what are the eating habits of cotylosaurs?
satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 10:32:07 AM
highlights in the evolution of vertebrates
satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 10:37:15 AM
snakes are meat eates because lizards are
snakes are meat eates because lizards are
satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 10:37:31 AM
how do snakes drink water?
satya - Wednesday, May 07, 2008 7:35:10 PM
a digression but a fascinating book